nbgrader: Automating Jupyter Notebook Grading
Introduction
Grading assignments in Jupyter Notebooks manually can be a tedious and inconsistent process. Nbgrader is an open-source tool designed to automate grading while still allowing manual feedback when necessary. It is widely used in educational settings, particularly for large-scale courses where efficiency and accuracy are critical.
With features like auto-grading, assignment distribution, and seamless integration with JupyterHub, nbgrader streamlines the workflow for both instructors and students. It supports various grading functionalities, such as predefined test cases, manual adjustments, and structured feedback, making it one of the most versatile grading solutions for Jupyter environments.
Key Use Cases
- Automating grading of coding assignments using predefined test cases.
- Providing structured feedback to students within Jupyter Notebooks.
- Managing assignments in large classes with seamless distribution and collection tools.
For a complete guide and tutorials, visit the official nbgrader documentation: nbgrader.readthedocs.io
Installation & Setup
Prerequisites
- Python (>=3.6)
- Jupyter Notebook or JupyterLab
- An existing JupyterHub setup (optional, but useful for multi-user environments)
Installation Steps
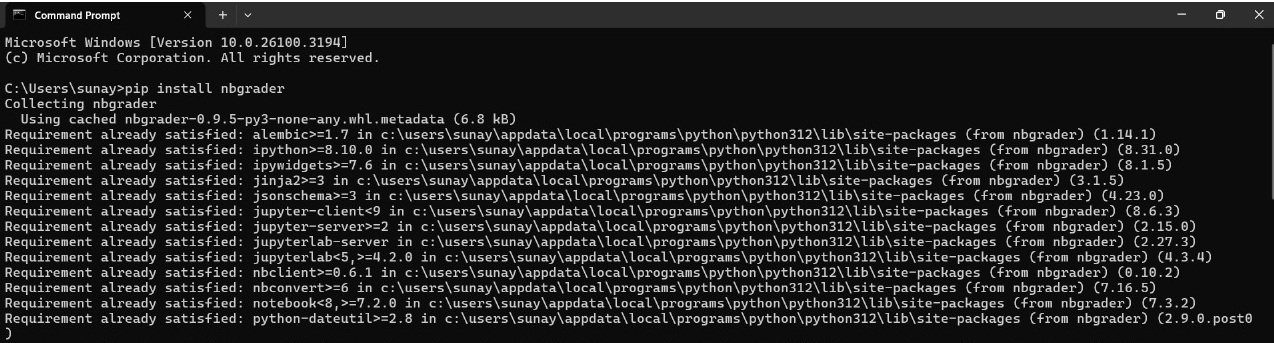
Install nbgrader via pip:
pip install nbgrader
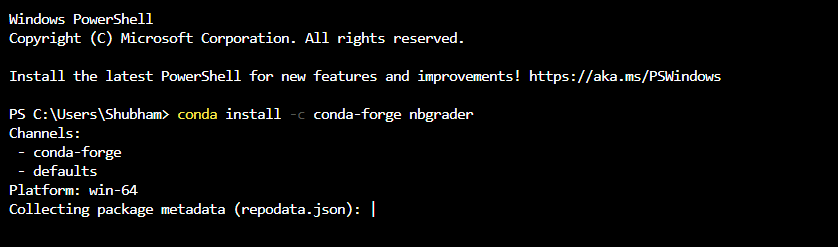
Or if you use Jupyter Notebook via Anaconda:
conda install -c conda-forge nbgrader
Configure nbgrader:
nbgrader quickstart es114
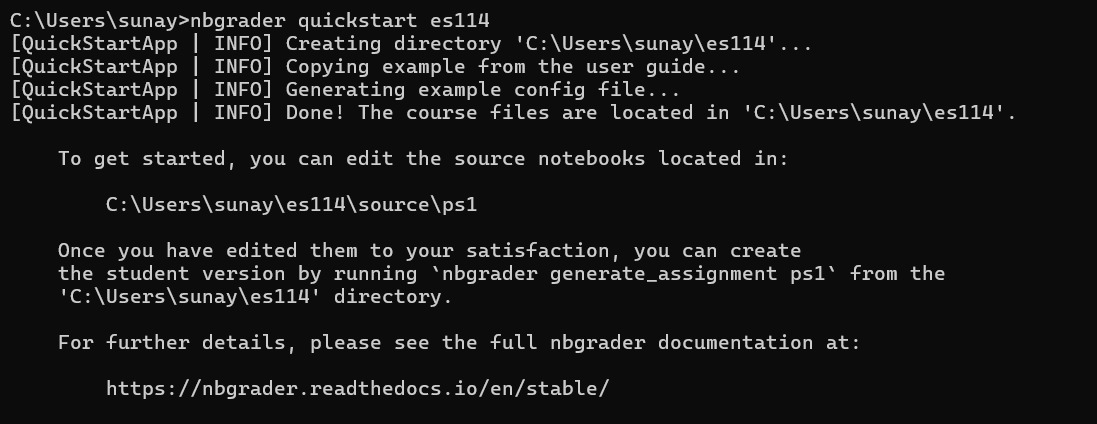
This sets up the necessary directory structure for an nbgrader course.
Creating assignments using code and API
1. Creating the assignment using API
You can create an assigment directly from the jupyter by clicking on + Add new assignment…
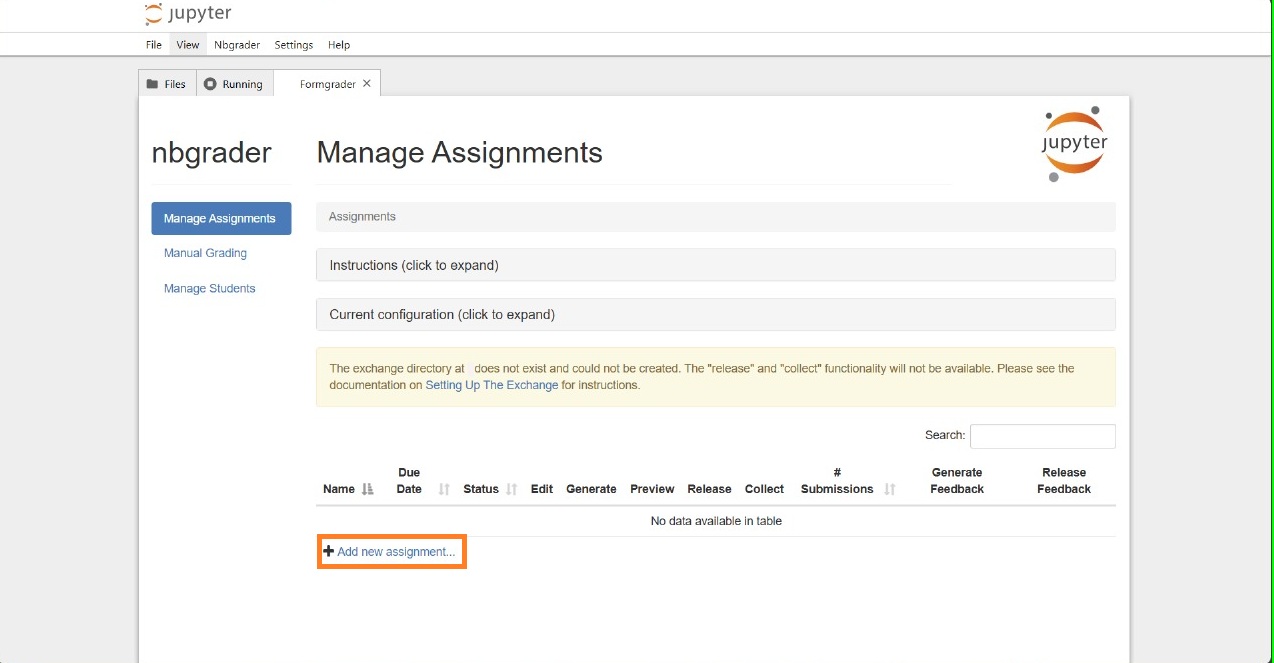
Then you can add the name and other details of the assignment.
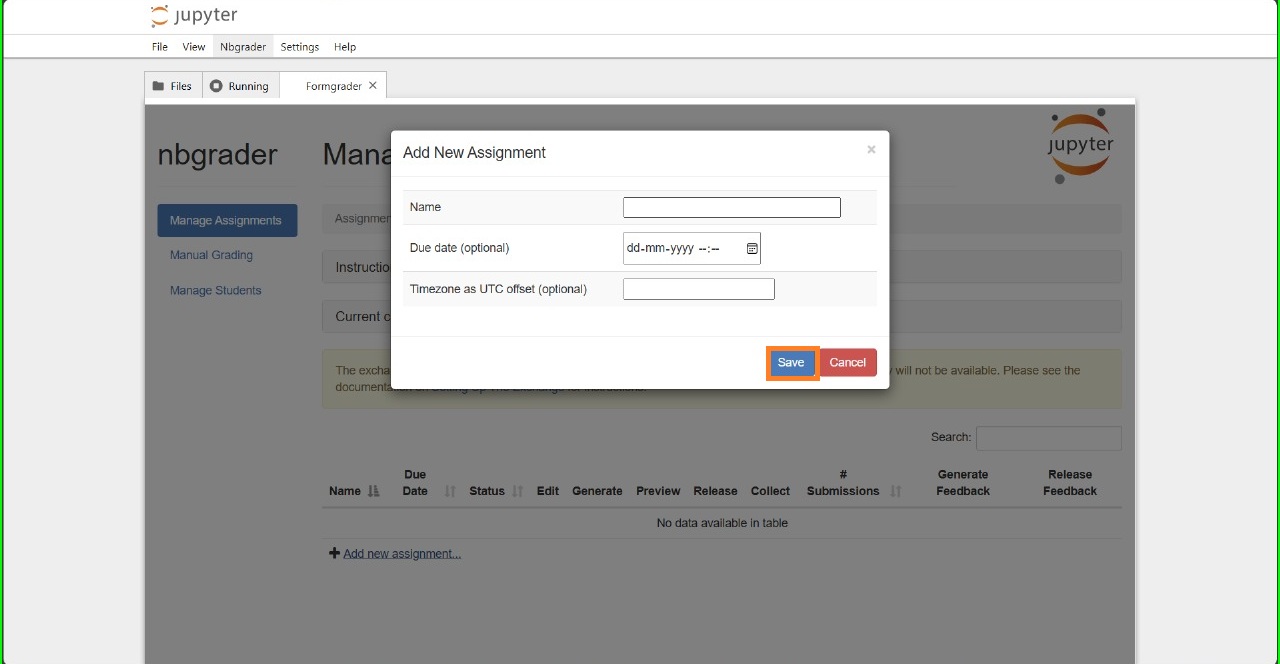
2. Creating assignments using terminal
You can also create the assignment by typing the following code in the terminal
nbgrader generate_assignment ps1
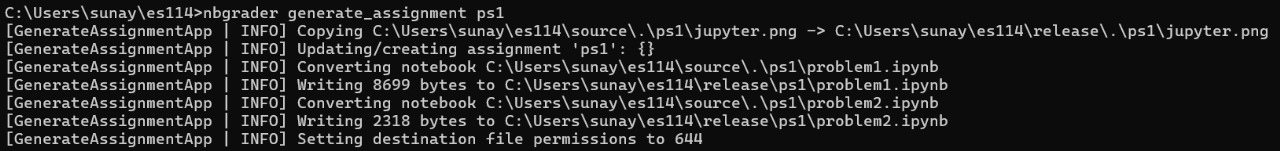 Here, ps1 is the name of the assignment.
Here, ps1 is the name of the assignment.
Key Features & Explanation
1. Automated Grading
Nbgrader allows instructors to create assignments with test cases that automatically evaluate student responses. This eliminates manual checking for objective questions, reducing grading time.
Example:
# Autograded answer
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b # Expected answer
# Test case
assert add_numbers(2, 3) == 5
2. Manual Grading & Feedback
For subjective responses, instructors can manually grade submissions and provide detailed feedback.
Example:
# Manually graded cell
feedback = "Great approach, but try optimizing your solution."
score = 8 # Adjust score manually
3. Assignment Management
Nbgrader streamlines the creation, release, and collection of assignments.
Example:
# Assign an exercise
nbgrader assign problem_set_1
# Collect student submissions
nbgrader collect
4. Integration with JupyterHub
Nbgrader seamlessly integrates with JupyterHub, ensuring assignments are securely managed without conflicts between students.
5. Version Control & Regrading
Nbgrader maintains different versions of student submissions, allowing instructors to track changes and regrade assignments if necessary.
Example:
# Regrade an assignment
nbgrader autograde problem_set_1 --force
6. Plagiarism Detection
Nbgrader can be combined with external tools like Turnitin or MOSS for academic integrity verification.
Code Examples
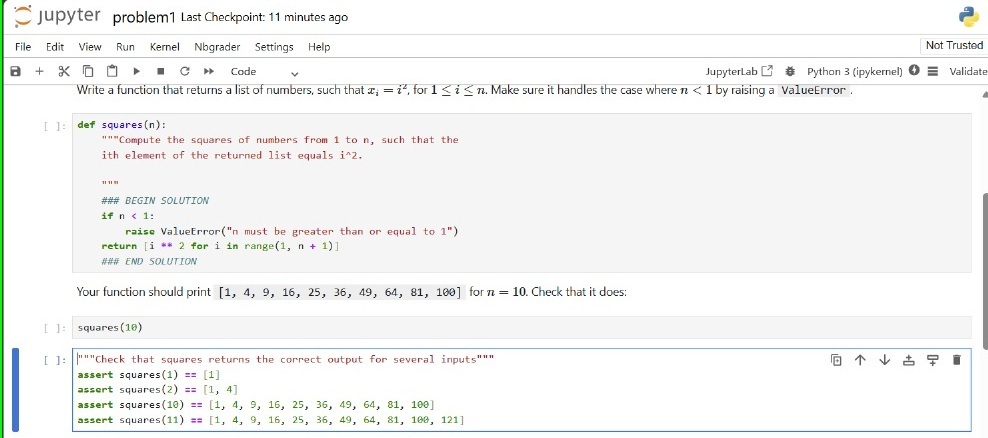
Creating an Auto-Graded Question
# Autograded answer
def squares(n):
"""Compute the squares of the numbers from 1 to n,
such that the ith element of the returned list equals to i^2."""
### BEGIN SOLUTION
if n<1:
raise valueError("n must be greater than or equal to 1")
return[i**2 for i in range(1, n+1)]
# Test case
assert square(3) == [9]
Releasing the assignment
You can release the assignment by clicking on the highlighted button.
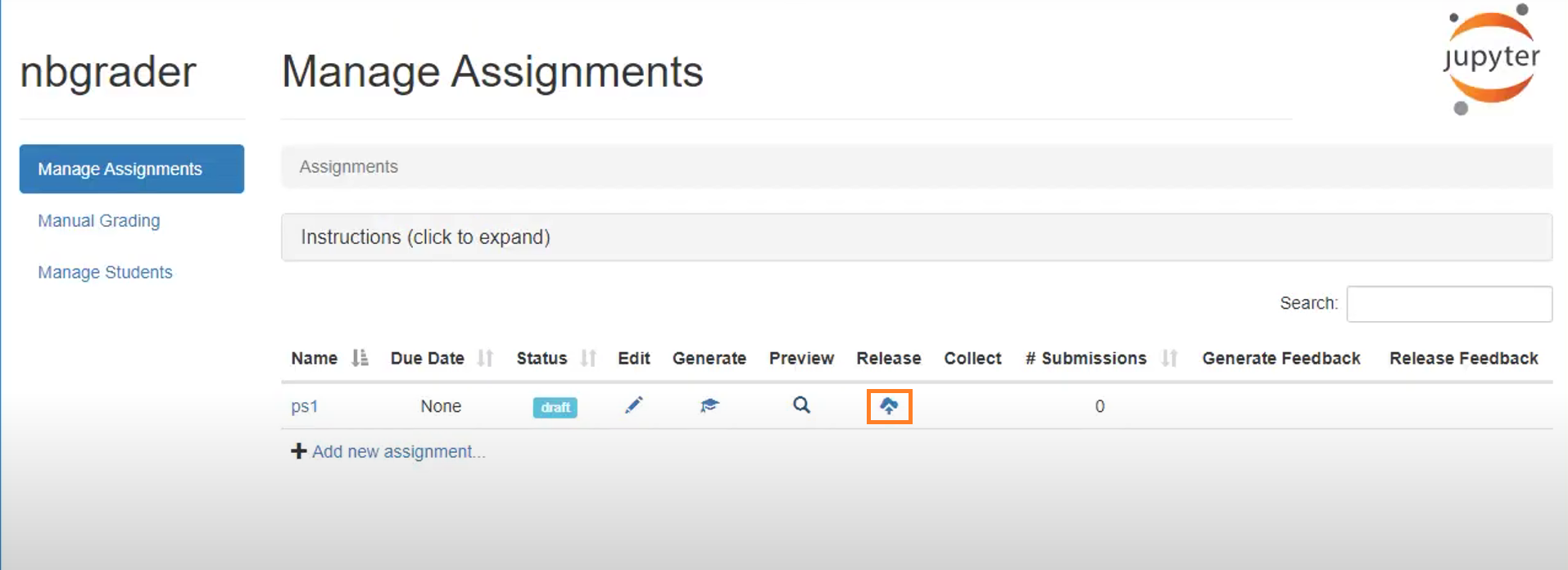
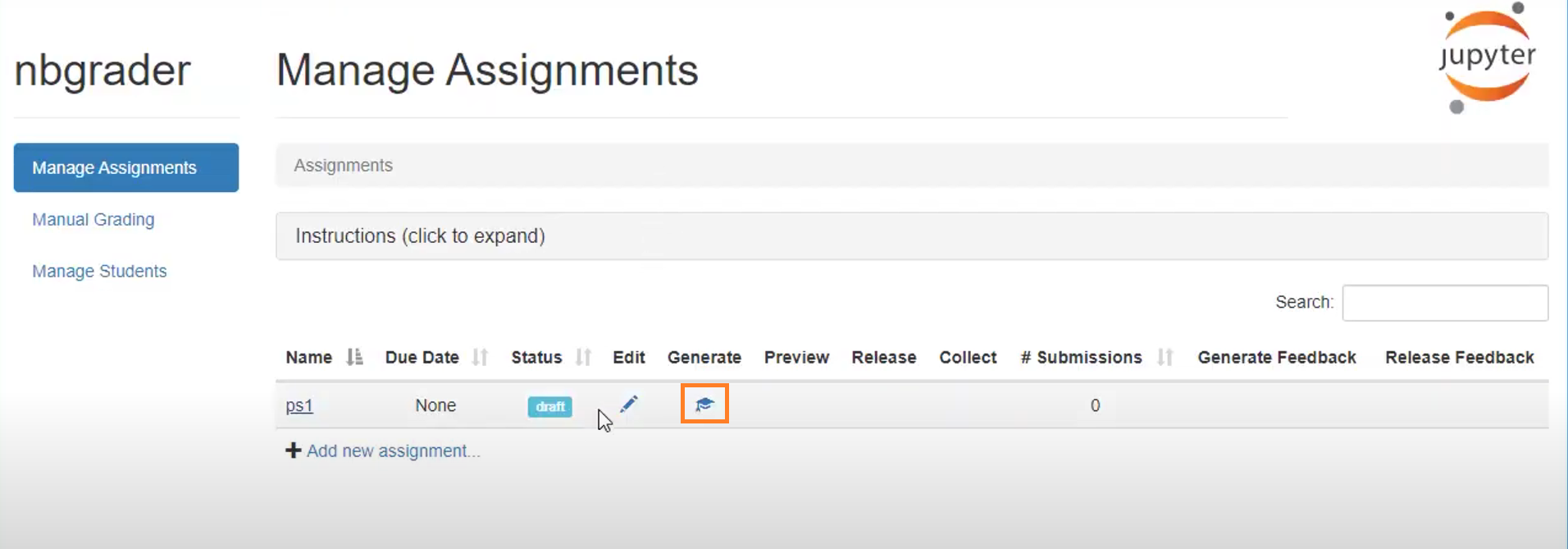 After that, it will successfully create the student version of the assignment. You can click on the highlighted button to release the assignment.
After that, it will successfully create the student version of the assignment. You can click on the highlighted button to release the assignment.
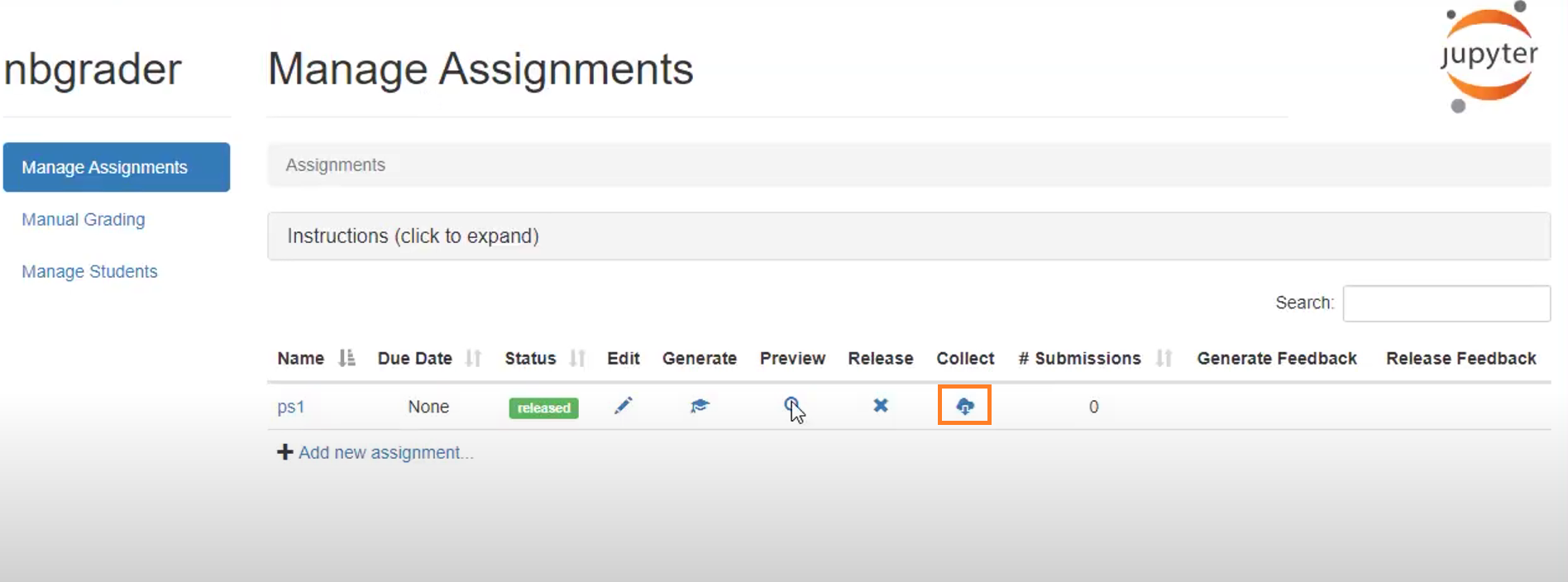
Collecting the assignment
Once the student submits the assignment, you can collect it by clicking on the highlighted button. This will reduce your work of manually collecting every assignment from each student.
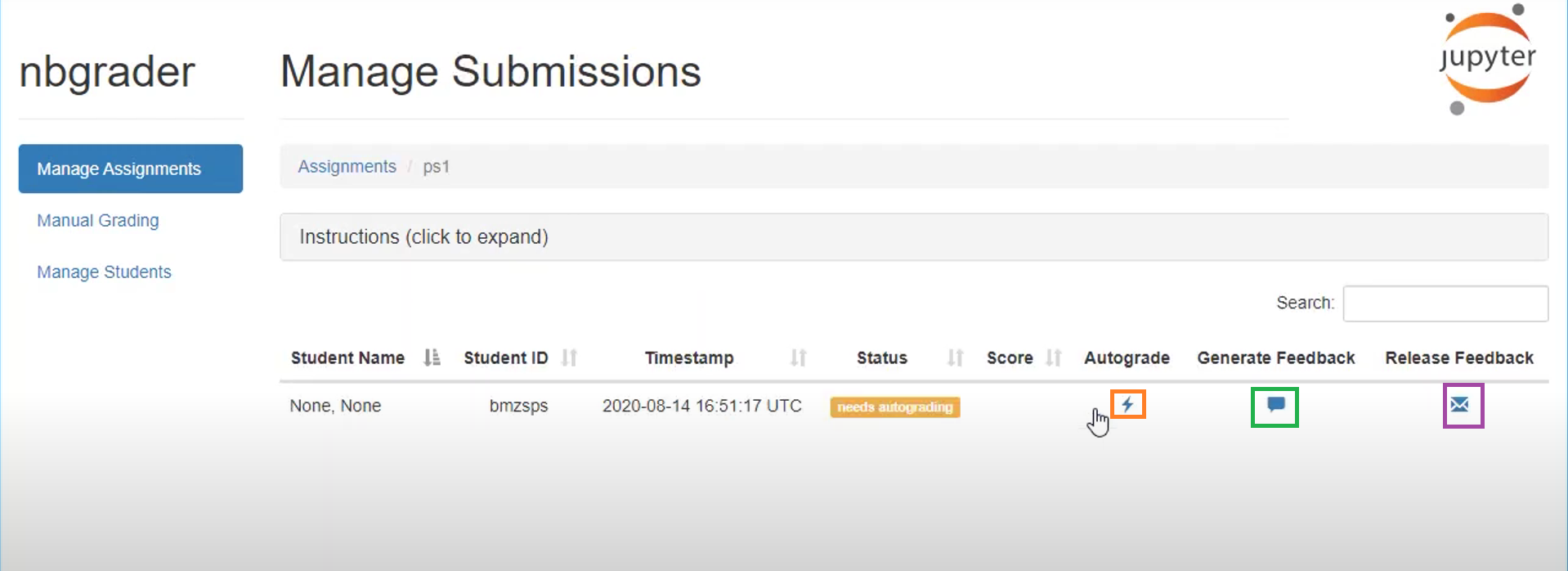
Grading and generating feedback for the assignment
Then, you can autograde/generate feedback/release feedback of the assignment by clicking on the highlighted button(s). Orange for autograde, green for generating feedback, and purple for releasing feedback. Source of image
Use Cases
1. University Courses
Used in university settings to evaluate large numbers of student assignments efficiently.
2. Coding Bootcamps
Automates exercises, tracks student progress, and offers structured coding challenges.
3. MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses)
Scales assignment evaluations without requiring a large teaching staff.
4. Corporate Training Programs
Used for assessing employee learning and progress in technical training programs.
5. Data Science & Machine Learning Workshops
Provides structured exercises with real-world datasets.
6. Research and Lab Work
Useful in scientific research and lab courses where experiments require structured assessment.
Conclusion
Overall, nbgrader is a powerful tool for automating assignment grading in Jupyter Notebooks. Its structured workflow simplifies assignment creation, collection, and evaluation, making it particularly useful for large-scale educational settings.
While nbgrader excels in auto-grading, its full potential is realized when integrated with other Python libraries, allowing for more sophisticated assessments. Its seamless integration with JupyterHub makes it a practical choice for scalable assessment solutions.